1. Low Level Data Oriented Programming
1-1. Struct Data Size
- aligns to the size of the biggest element - defining small members next to each other saves padding
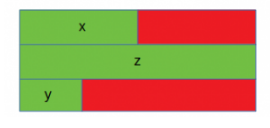
- ex1)
// 24 Byte - alignment: 8byte(=max(4, 8, 2))
struct A {
int x; // 4 byte, padded to 8 byte
double z; // 8 byte
short int y; // 2 byte, padded to 8 byte
}
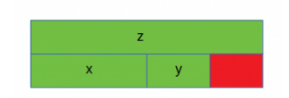
- ex2)
// 16 Byte
struct B {
double z; // 8 byte
int x; // 4 byte, aligned with y
short int y; // 2 byte, aligned with x
}
1-2. Data-driven “OR” Structure - Index over address, Encoding Approach
Modern C and other languages have enum types that help save optional data members when they are not needed.
- For example, say there is a Person struct as below:
/// 24 byte for all 100% of people, even though only 20% of people are adults and have driver's licence.
/// If there is 1024 people, 24 Byte * 1024 = 24KB
struct Person {
int id
int age
Country country
const Country { Korea, Japan }
// optional data - only adults have it, which is 20% of the whole population
DriversLicense license;
struct DriversLicense {
int year_acquired
int month_acquired
int day_acquired
};
}
- Based on our “observation of Data” that “only 20% of the population is adult” and “There are only two nationality to the whole population: Korean and Japanese”, we can plan optimization for the Person Struct - dividing the Person into Adult and Non-adult will result in significant memory save.
-
to do this, we can encode people into four different enum categories, saving data when the person belongs to a category that doesn’t have driver’s license. ```Cpp // Data observation 1: There are only two nationalities: Korean and Japanese // Data observation 2: Only 20% of the whole population have Driver’s License // Data observation 3: driver’s license only have members of same size - no danger for overpadding for alignment. struct Person { Tag tag Common common
const Tag = enum { KoreanWithDriversLicense, // 25 byte KoreanWithoutDriversLicense, // 13 byte JapaneseWithDriversLicense, // 25 byte JapaneseWithoutDriversLicense // 13 byte }
const Common = struct { int id int age usize_t extra_index }
const DriversLicense = struct { int year_acquired int month_acquired int day_acquired } }
// When 1024 people, // population size: 13 byte * 1024 = 13KB var population: MultiArrayList(Person) // population_with_drivers_license size: 25 byte * 128 = 3.125KB var population_with_drivers_license: ArrayList(Person.DriversLicense)
// Total Memory: 16.125KB = 33% memory save ```