Basic of Marketing - Building Strong Brands

- Seller’s Market: Product Focused Market - Develop that product as best as possible.
- business focus: sell as much as you can - profit = volume(market share)
- key consideration: How to get growth? - new products based on experience? new markets?
- inside-out
- Customer’s Market: How to make customers buy to me rather than competitors - look at what “the customer wants”
- outside-in
- Which Customer? - We can’t satisfy everyone - PICK AND CHOOSE. - Pick the target customer group and deliver exactly what that group wants.
- profit = value creation - Not one transaction, we need to create value time after time after time - customer loyalty, constantly delivering value over time
Market vs Customer Share
- Market share: try to get a little bit from everybody
- Customer share: A more narrow market - try to get more from each of those target customer’s markets - loyalty
Loyalty is profitable
- It is a cumulative result of delivering a group of user’s needs consecutively
- First time figuring out needs and delivering is hard, but after that the iterations get easier.
- Easier to retain customers than to add new ones
- Not only sell one product, cross sell around the already going-well product. - **Increasing customer share.
ex) GAP or Jeans Shop: Also sell belt
Globalization Changes the Market Place
- Not a 1-1 conversation(customer-producer) anymore - internet, social media, … - customers can talk to customers
- Good and bad - they propagate good and the bad.
- Not only value, but top-notch customer experience.
Customer Experience
- starts before the transaction, ends after the transaction
- ex) finding location, parking, buy, and then leaving - the entire process
- Marketer has to be transparent, authentic, and think of all the customer experience.
Changes after the Recession
- People stopped trusting market
- Build trust based on authentic, trust, discipline genuine customer value.
- Not only deliver customer value over time/experiential way, -> Cut costs and deliver value in discipline manner , flexible to change

3 Principles of Marketing
1) Principle of Customer Value - Provide real, genuine customer value 2) Principle of Differentiation - Provide what the customer wants, but better than your competition 3) Principle of Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning - Select specific group you want to satisfy
4 P’s of Marketing
1) Product - Seller puts in exchange 2) Place - Method of distribution. 3) Promotion - Way Seller communicates the benefits of product 4) Price - Buyer puts in exchange
- Also can be used in non-market ex) American Red Cross 1) Product: Little sticker 2) Place: Blood mobile 3) Promotion: Missing class 4) Price: Blood
Strategic Marketing
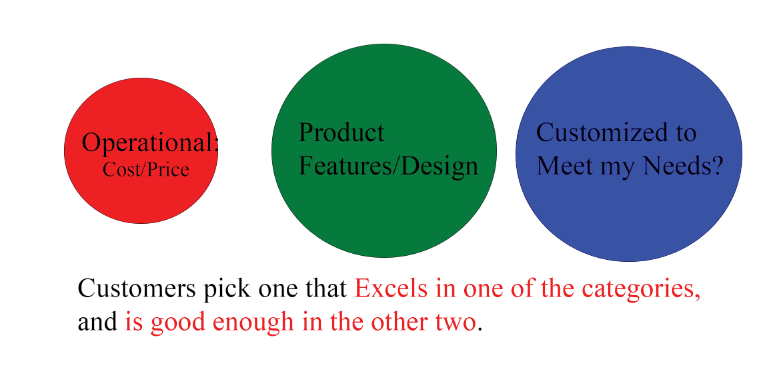
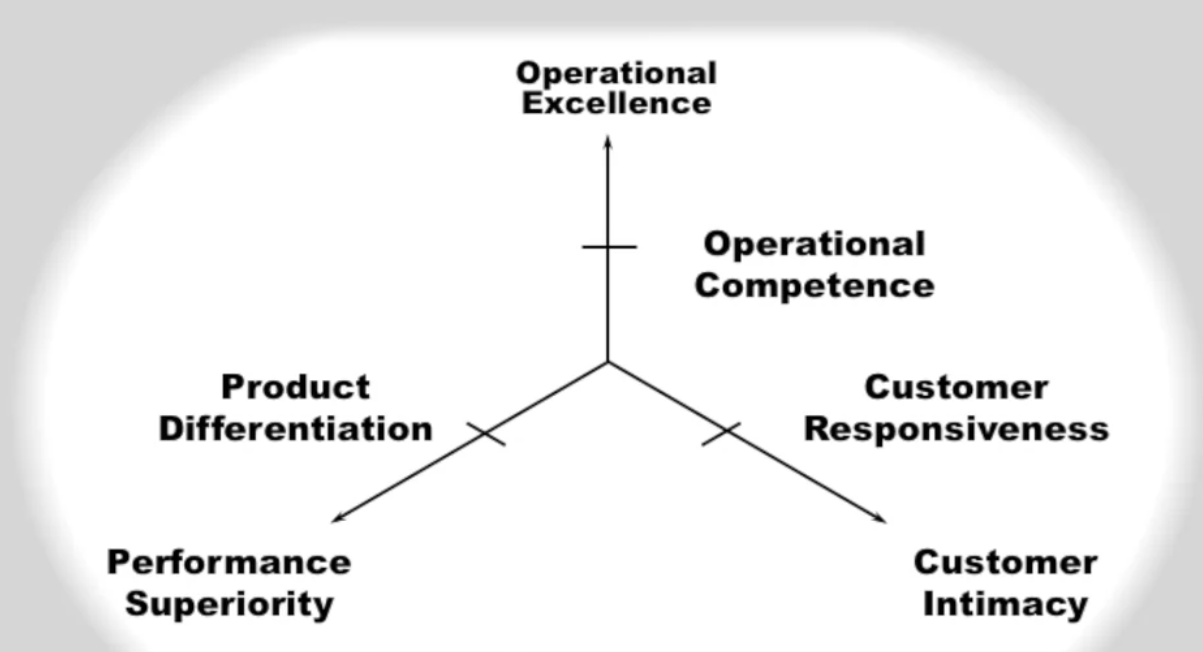
- Choose which of the three categories we will excel at and be the first in the market to deliver that goal.
- Depending on which category we chose, our hiring/resource/and other implications change greatly. 1) Figure out how much of each category our market is able to differentiate 2) Figure out fair value of each category in our market. - market research
- In mature markets, many products are above fair value in all categories - hard to search 3) Where the competitors are in each axis.
Short term != Long term
- long term: excel Customer intimacy
- short term: our Operational excellence is not fair value, so first prioritize in improving that.
fair value
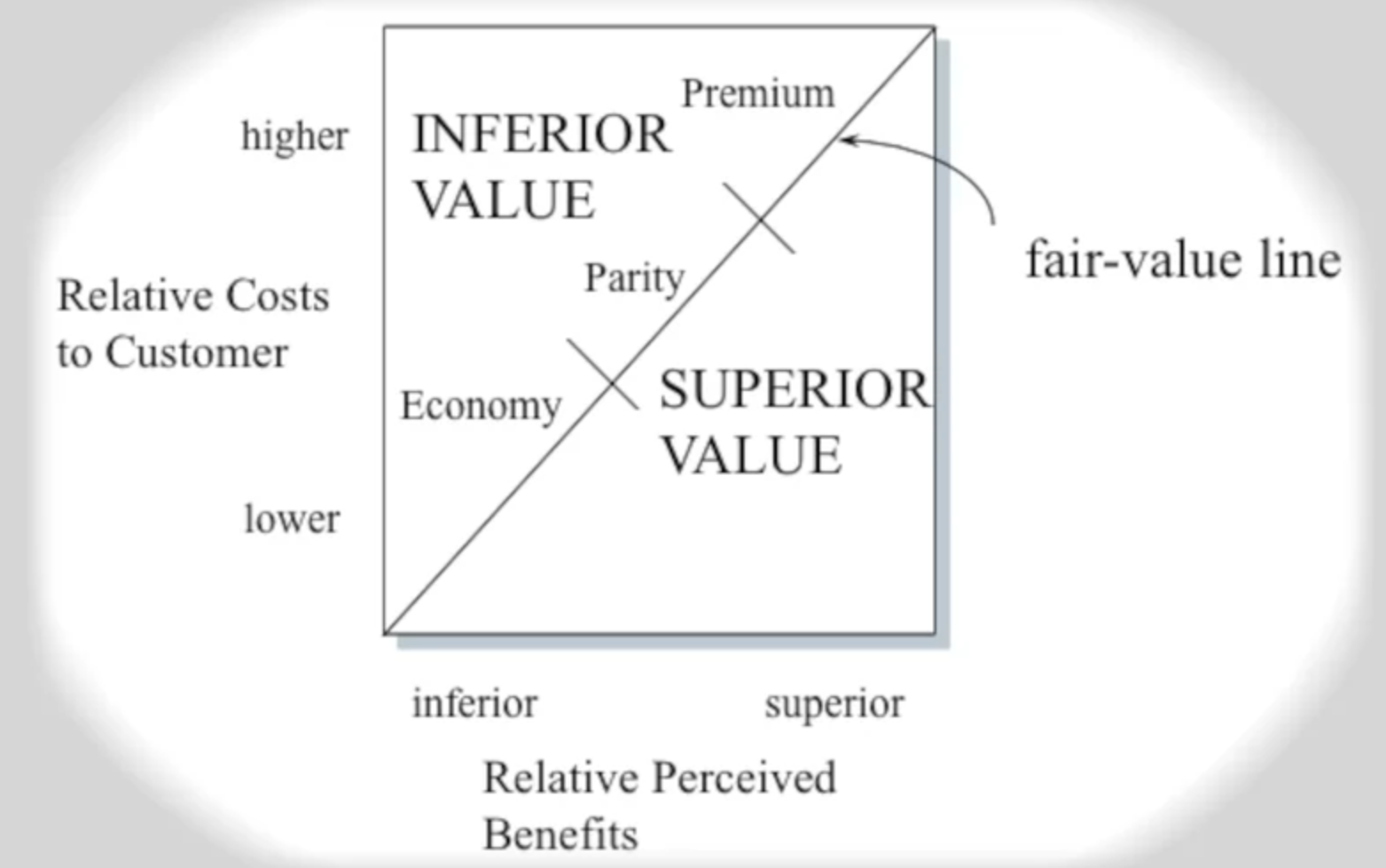
- If you offer more benefits, customers are willing to pay higher price
- If you offer lower price, customers will expect fewer benefits, as long as what you offer appears to be fair(it still has the key superior values)
- We need to offer fair value in two of these offers, but something better than fair value in one of the categories
but of course, competitors keeps advancing, so the cut for fair value and better than fair value keeps going up
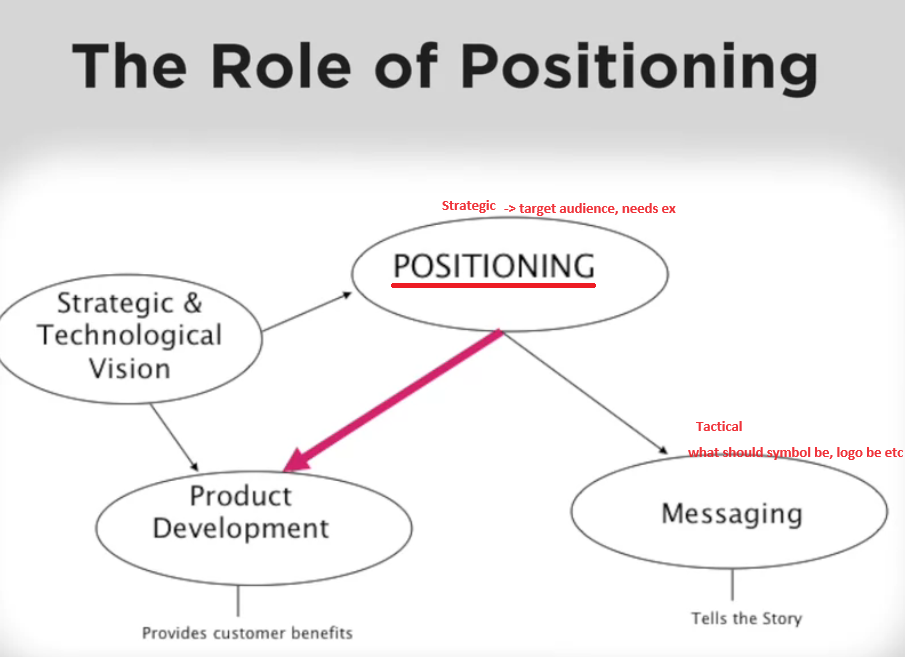
Positioning Process
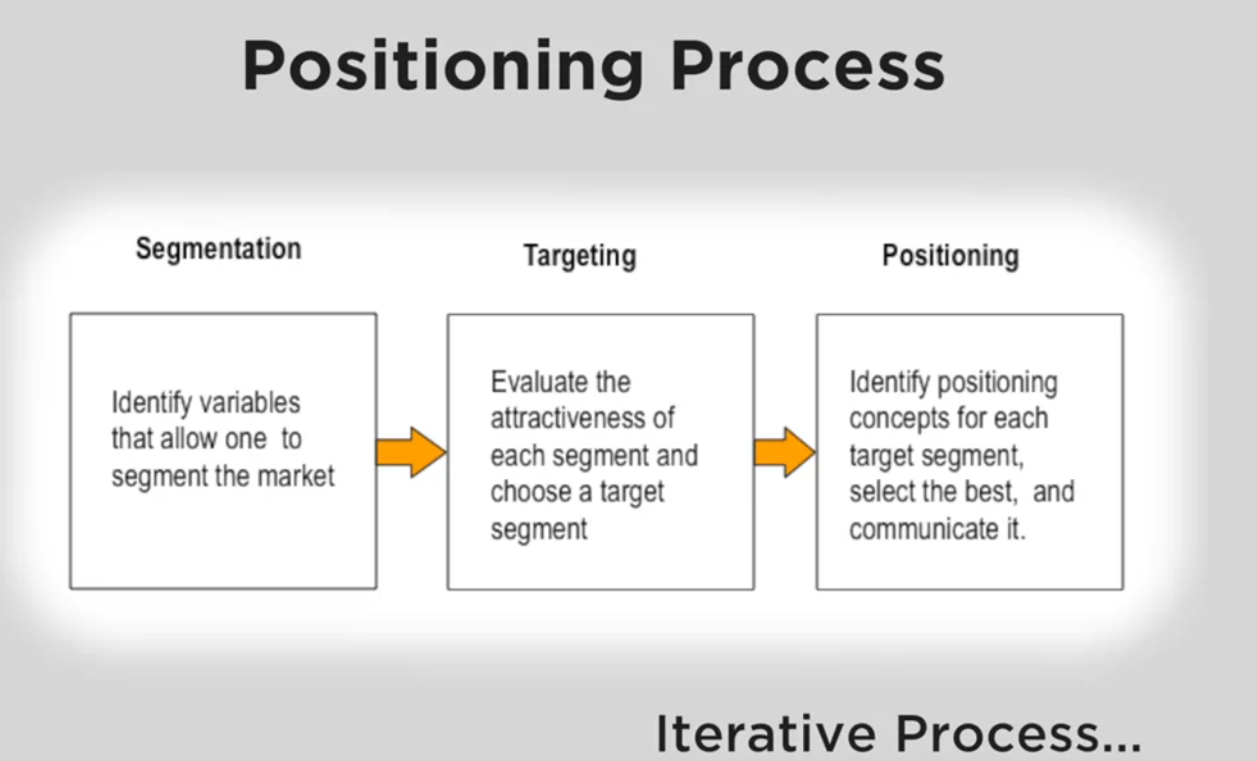
- If you don’t segment and meet specific need, you tend to cut cost and go for the average value, not satisfying anyone.
How to Divide?
1) Characteristic of Customer - Demographic ex) man/woman, rich/poor 2) Benefits Sought -> ex) running shoes -> comfort/aesthetics/technology 3) How do people purchase -> Ex) Online, Physical stores, Phone, loyal, once a month
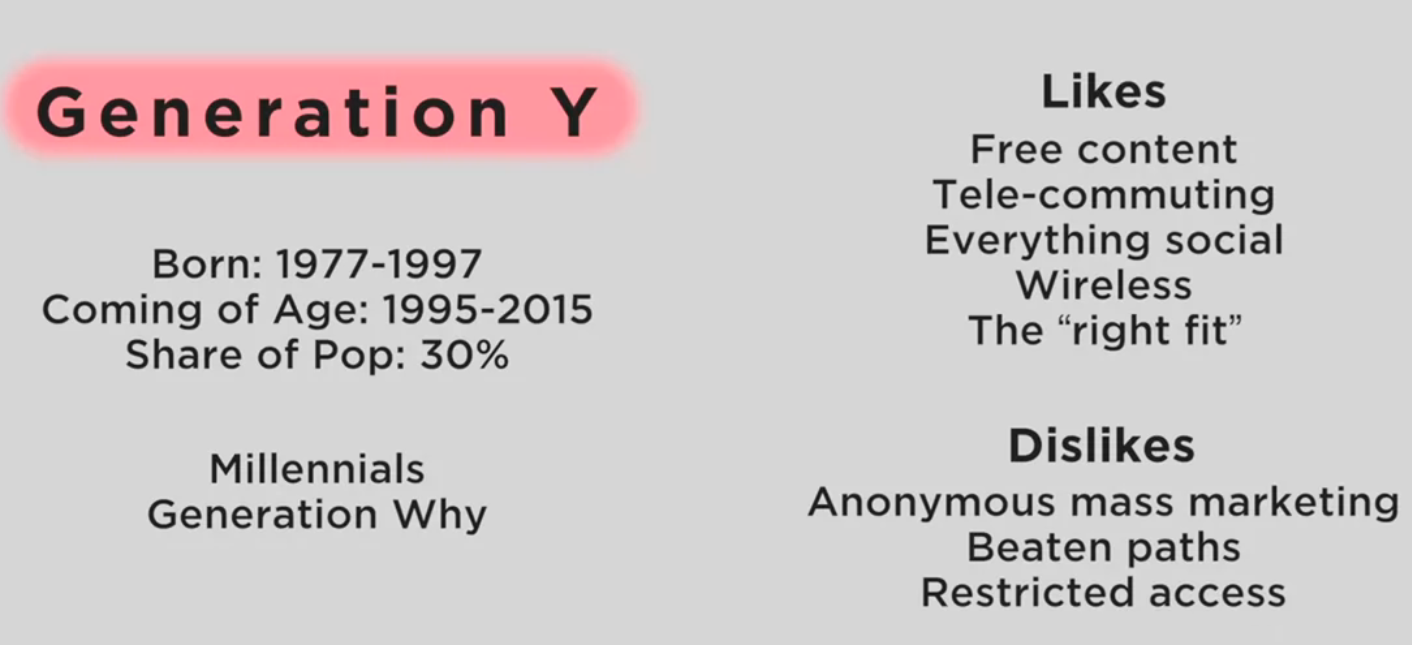
Cohort Analysis: Life experience of the same generation
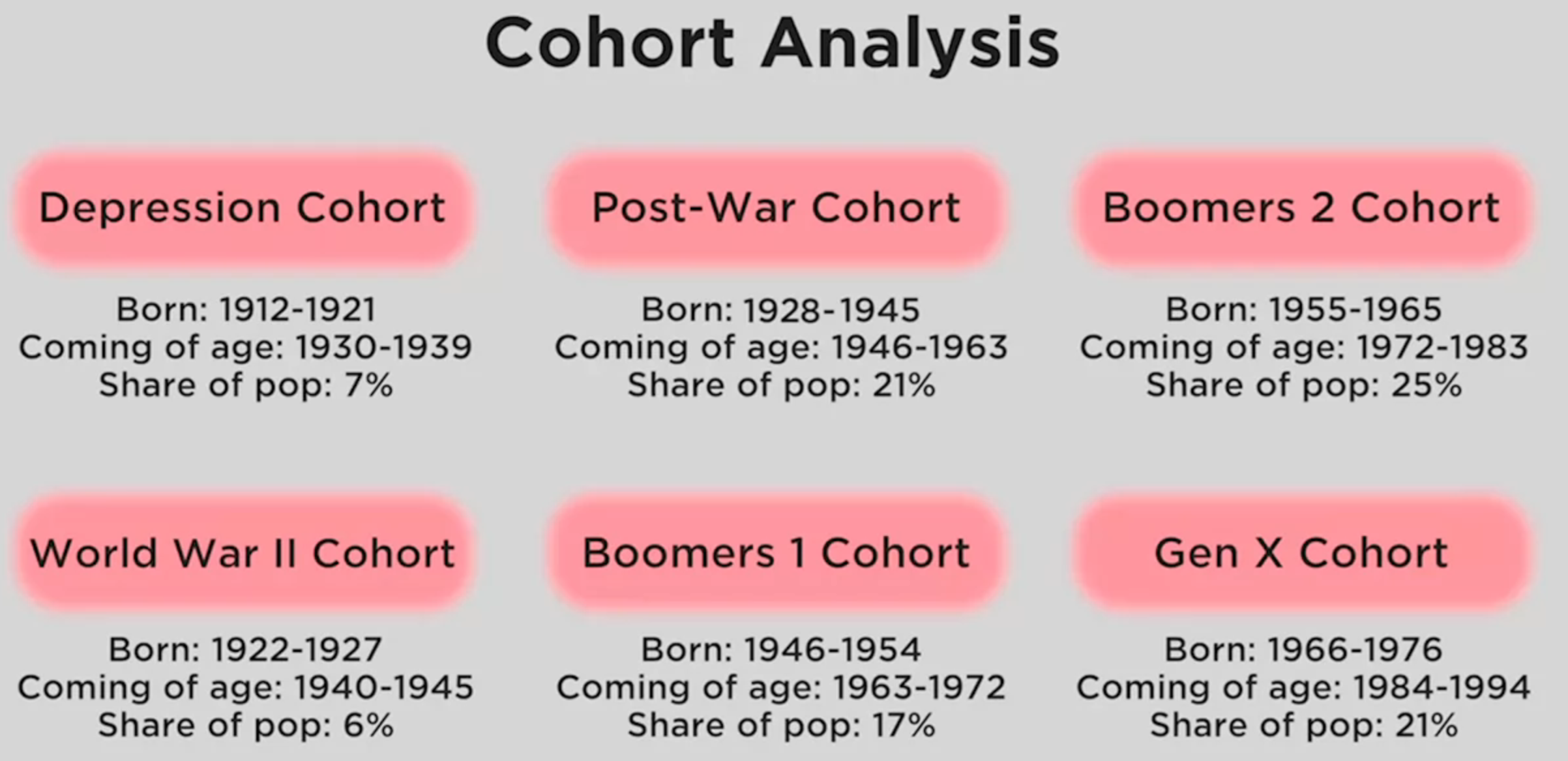
why interested in millenials? -> when a generation is coming of age, their purchases are likely to make them loyal.

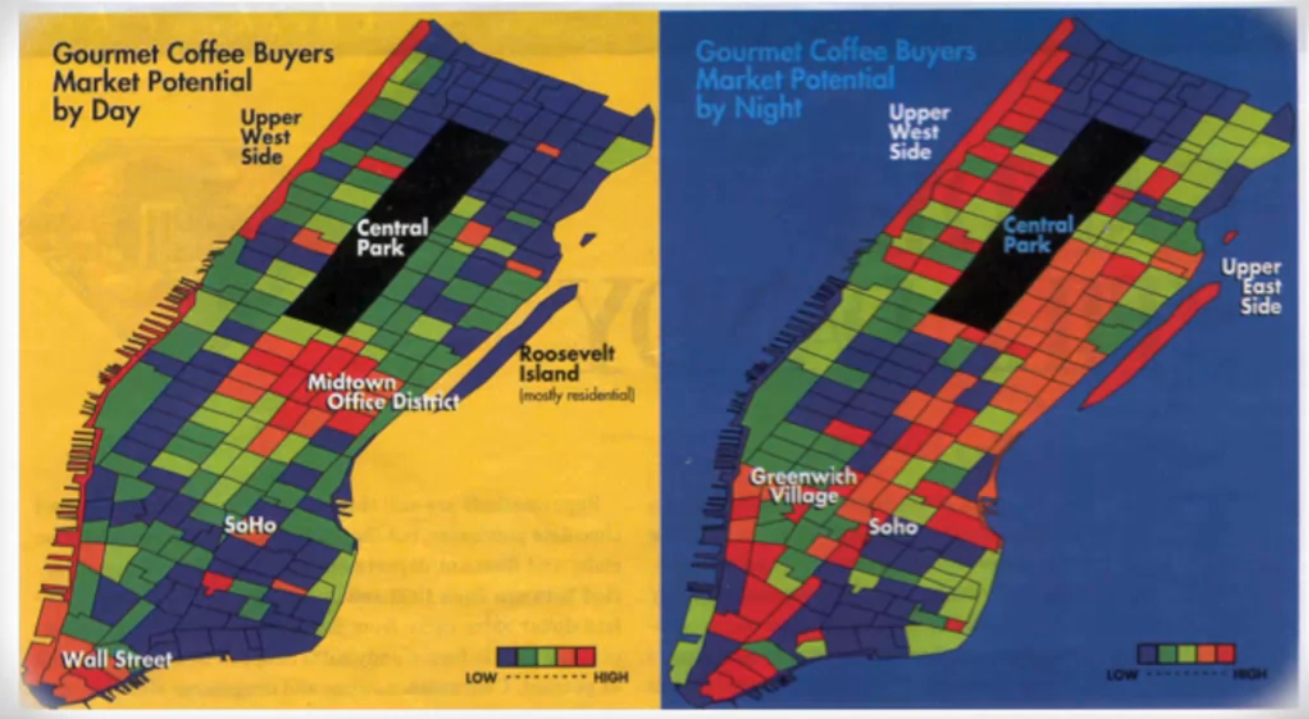
Geographic Segmentation(Clustering) - PRIZM
- People who live are similar near tend live near each other - not by where they are - ex) California cluster can have people that live in Europe
- Zip clustering: Zip code
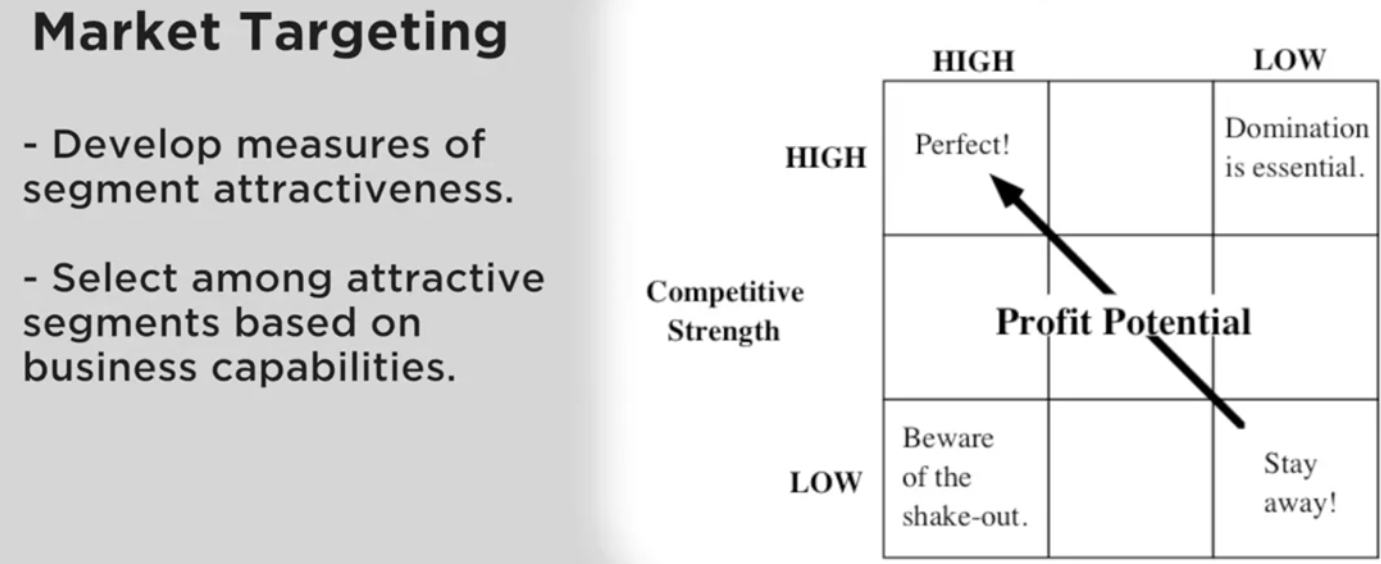
Segment Selection Criteria

Brand Positioning
Essence of the brand (P of STP)
What is a Brand?
whatever the customer think the brand is
strong branding message ex) Disney -> then hopefully your desired message = customer message if message isn’t strong, and customer image != your desired image, customer wins - their image is your brand

Positioning Statement
- Target Segmenting
- Point of Difference
- Frame of Reference: Other competitors they are comparing themselves to.

- Frame of Reference changes based on which competitor you compare to(ex) PS5 as a hardware spec vs available games)
- defensive: you own and can’t copy easily
Point of Parity
1) Category POPs: Something you must have to be considered fit for this frame of reference. ex) grocery store: must have certain fresh products(egg, milk, etc).
2) Competitive POPs: negate competitor’s point of difference ex) Mac has 8 cores, when others have 4 cores? -> We make 8core CPU, their point of difference is gone.
SCA: Sustainable Competitive Advantage
ex) Apple computer -> Mac: Frame of reference => computer to consumer electronics
POD criteria
- Desirable to customer?
- Can you deliver to customer?
Brand Mantra
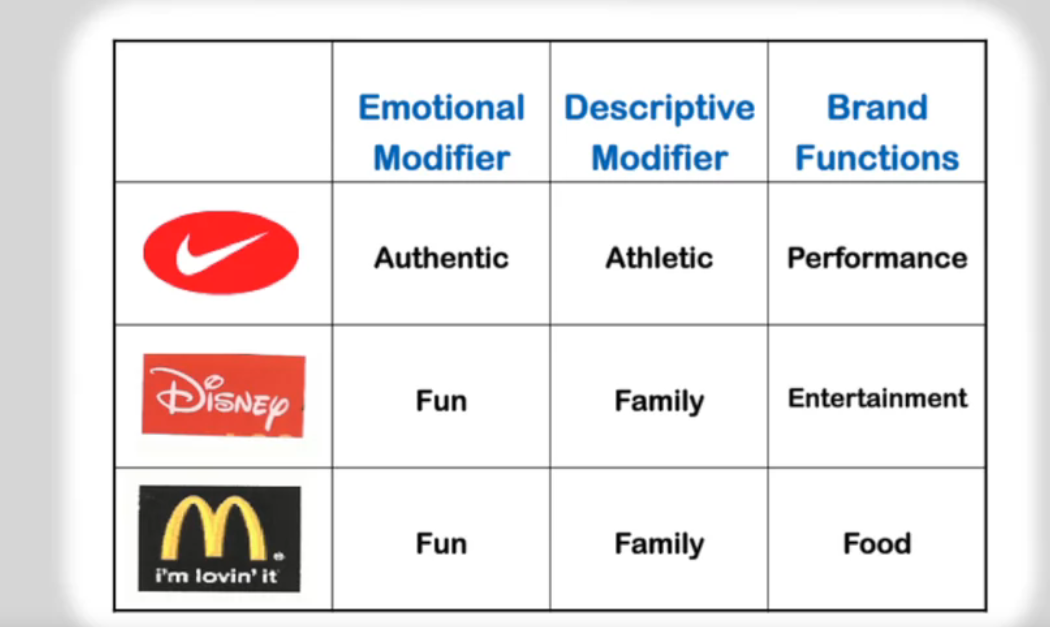

- Very sharp, needs to be in 30 seconds
Experiential Branding
Brand notion is not enough. Define all the experience related to the brand. notions are Very emotional
Today’s rich brand are not just differentiated; they are experientially differentiated -> not a single promise, but a relationship.

- Multisensoral Positioning - smell? feel? - distinct from anybody else
- Experientail Brand Value Promise: specific experiences the brand gives to customers - sense, feel(happy? tragic?), think, act, relate